Appearance
threejs雷达扫描效果
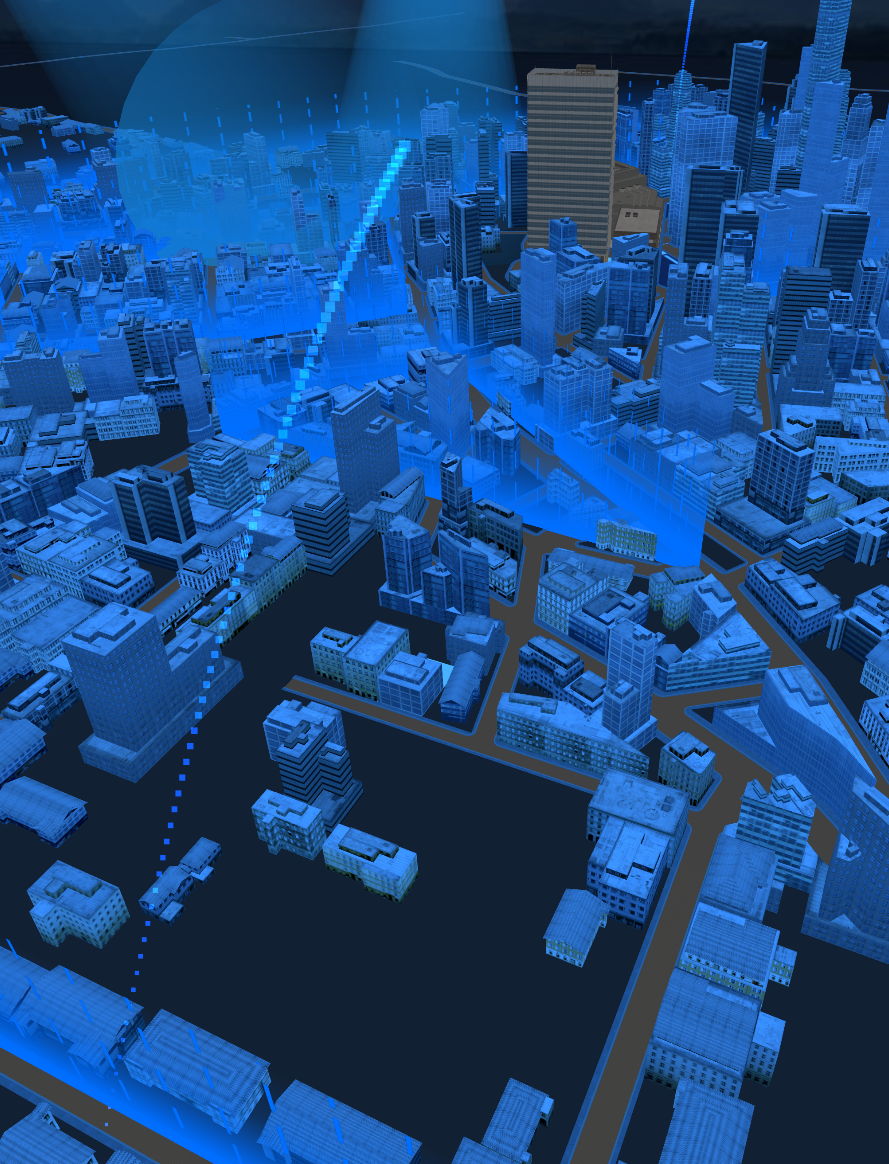
在Three.js中,实现一个圆形扫描效果可以为场景增添一种科技感,常见于雷达扫描、数据可视化或特殊视觉效果的展示。本文将详细介绍如何使用Three.js和自定义着色器来创建这样的动态圆形扫描效果。
创建圆形扫描效果的步骤
1. 编写自定义片元着色器: 自定义片元着色器中定义了 atan2函数来计算角度,以及根据时间和位置变化来调整像素的透明度,从而实现扫描效果。
2. 定义着色器uniform变量: 在着色器代码中定义了控制颜色、时间、透明度、半径和扫描线宽度的uniform变量。
3. 创建平面几何体: 使用 THREE.PlaneGeometry创建一个平面作为显示扫描效果的载体。
4. 设置ShaderMaterial材质: 创建 THREE.ShaderMaterial材质实例,传入自定义的顶点和片元着色器代码,并设置uniform变量。
5. 创建Mesh网格: 使用几何体和材质创建 THREE.Mesh网格,设置网格的位置和旋转,以适应动画需求。
6. 动画效果实现: 在动画循环中更新uniform变量 time的值,以实现随时间变化的扫描效果。
js
import * as THREE from 'three';
const frag_basic = `
precision mediump float;
float atan2(float y, float x){
float t0, t1, t2, t3, t4;
t3 = abs(x);
t1 = abs(y);
t0 = max(t3, t1);
t1 = min(t3, t1);
t3 = float(1) / t0;
t3 = t1 * t3;
t4 = t3 * t3;
t0 = -float(0.013480470);
t0 = t0 * t4 + float(0.057477314);
t0 = t0 * t4 - float(0.121239071);
t0 = t0 * t4 + float(0.195635925);
t0 = t0 * t4 - float(0.332994597);
t0 = t0 * t4 + float(0.999995630);
t3 = t0 * t3;
t3 = (abs(y) > abs(x)) ? float(1.570796327) - t3 : t3;
t3 = (x < 0.0) ? float(3.141592654) - t3 : t3;
t3 = (y < 0.0) ? -t3 : t3;
return t3;
}
// 计算距离
float distanceTo(vec2 src, vec2 dst) {
float dx = src.x - dst.x;
float dy = src.y - dst.y;
float dv = dx * dx + dy * dy;
return sqrt(dv);
}
#define PI 3.14159265359
#define PI2 6.28318530718
uniform vec3 u_color;
uniform float time;
uniform float u_opacity;
uniform float u_radius;
uniform float u_width;
uniform float u_speed;
varying vec2 v_position;
`
const Shader = {
vertexShader: `
varying vec2 v_position;
void main() {
v_position = vec2(position.x, position.y);
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * modelViewMatrix * vec4(position, 1.0);
}`,
fragmentShader: `
${frag_basic}
void main() {
float d_time = u_speed * time;
float angle = atan2(v_position.x, v_position.y) + PI;
float angleT = mod(angle + d_time, PI2);
float width = u_width;
float d_opacity = 0.0;
// 当前位置离中心位置
float length = distanceTo(vec2(0.0, 0.0), v_position);
float bw = 5.0;
if (length < u_radius && length > u_radius - bw) {
float o = (length - (u_radius - bw)) / bw;
d_opacity = sin(o * PI);
}
if (length < u_radius - bw / 1.1) {
d_opacity = 1.0 - angleT / PI * (PI / width);
}
if (length > u_radius) { d_opacity = 0.0; }
gl_FragColor = vec4(u_color, d_opacity * u_opacity);
}`
}
/**
* 创建一个THREE.Mesh对象
*
* @param opts 配置项
* @param opts.radius 半径,默认为50
* @param opts.color 颜色,默认为"#fff"
* @param opts.speed 速度,默认为1
* @param opts.opacity 透明度,默认为1
* @param opts.angle 角度,默认为Math.PI
* @param opts.position 位置,默认为{x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
* @param opts.rotation 旋转角度,默认为{x: -Math.PI / 2, y: 0, z: 0}
* @returns 返回一个THREE.Mesh对象
*/
export default function (opts) {
const {
radius = 50,
color = "#fff",
speed = 1,
opacity = 1,
angle = Math.PI,
position = {
x: 0,
y: 0,
z: 0
},
rotation = {
x: -Math.PI / 2,
y: 0,
z: 0
}
} = opts;
const width = radius * 2;
const geometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(width, width, 1, 1);
const material = new THREE.ShaderMaterial({
uniforms: {
u_radius: {
value: radius
},
u_speed: {
value: speed
},
u_opacity: {
value: opacity
},
u_width: {
value: angle
},
u_color: {
value: new THREE.Color(color)
},
time: {
value: 0
}
},
transparent: true,
depthWrite: false,
depthTest: false,
side: THREE.DoubleSide,
vertexShader: Shader.vertexShader,
fragmentShader: Shader.fragmentShader,
})
const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
mesh.rotation.set(rotation.x, rotation.y, rotation.z);
mesh.position.copy(position);
return mesh
}使用案例
js
import Radar from './radar.js'
let uTime = {
value:0,
}
const radarData = {
position: {
x: 23,
y: 10,
z: 268,
},
radius: 20,
color: "#ff0000",
opacity: 0.5,
speed: 2,
};
const radarMesh = Radar(radarData);
radarMesh.material.uniforms.time = uTime;
const clock = new THREE.Clock(); //计时器
const FPS = 60; // 指的是 30帧每秒的情况
const singleFrameTime = 1 / FPS;
let timeStamp = 0;
function animate() {
window.loopId = requestAnimationFrame(animate);
const delta = clock.getDelta(); //获取距离上次请求渲染的时间
uTime.value += delta;
if (timeStamp > singleFrameTime) {
renderer.render(scene, camera);
// 剩余的时间合并进入下次的判断计算 这里使用取余数是因为 当页页面失去焦点又重新获得焦点的时候,delta数值会非常大, 这个时候就需要
timeStamp = timeStamp % singleFrameTime;
}
}效果展示
 小江的网站
小江的网站