Appearance
threejs动态飞线效果
在数据可视化和科学可视化领域,动态飞线(或称流线)常用于表示两点之间的流动或连接。本文将介绍如何在Three.js中创建并实现这种效果,通过自定义着色器和动画技术,让飞线动起来。
创建动态飞线效果的步骤
1. 定义飞线路径: 使用 THREE.QuadraticBezierCurve3二次贝塞尔曲线来定义飞线的基本形状。贝塞尔曲线为飞线提供了平滑的曲线路径。
2. 计算飞线粒子位置: 在贝塞尔曲线上根据指定的密度采样点,这些点将作为飞线的粒子位置。
3. 设置粒子属性: 为每个粒子设置属性,如在曲线上的相对位置和索引,这些属性将用于控制粒子的显示顺序和动画。
4. 创建粒子几何体: 使用 THREE.BufferGeometry存储粒子的位置和其他属性,如索引和当前序号。
5. 编写自定义着色器: 自定义顶点着色器和片元着色器,控制粒子的颜色、大小和透明度,实现动态效果。
6. 动画粒子: 在动画循环中,根据时间和其他动态因素更新粒子的属性,如大小和透明度,实现飞线的动态流动效果。
js
import * as THREE from 'three';
/**
* 获取三维粒子位置并返回粒子对象
*
* @param option 配置项对象
* @param option.source 起始点坐标对象,包含x, y, z属性
* @param option.target 目标点坐标对象,包含x, y, z属性
* @param option.height 粒子高度
* @param option.size 粒子大小
* @param option.color 粒子颜色
* @param option.range 显示当前范围的粒子个数
* @returns 粒子对象
*/
export default function (option) {
const {
source,
target,
height,
size,
color,
range
} = option;
const positions = [];
const attrPositions = [];
const attrCindex = [];
const attrCnumber = [];
const _source = new THREE.Vector3(source.x, source.y, source.z);
const _target = new THREE.Vector3(target.x, target.y, target.z);
const _center = _target.clone().lerp(_source, 0.5);
_center.y += height;
const number = parseInt(_source.distanceTo(_center) + _target.distanceTo(_center));
const curve = new THREE.QuadraticBezierCurve3(
_source,
_center,
_target
);
const points = curve.getPoints(number);
// 粒子位置计算
points.forEach((elem, i) => {
const index = i / (number - 1);
positions.push({
x: elem.x,
y: elem.y,
z: elem.z
});
attrCindex.push(index);
attrCnumber.push(i);
})
positions.forEach((p) => {
attrPositions.push(p.x, p.y, p.z);
})
const geometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry();
geometry.setAttribute('position', new THREE.Float32BufferAttribute(attrPositions, 3));
// 传递当前所在位置
geometry.setAttribute('index', new THREE.Float32BufferAttribute(attrCindex, 1));
geometry.setAttribute('current', new THREE.Float32BufferAttribute(attrCnumber, 1));
const shader = new THREE.ShaderMaterial({
transparent: true,
depthWrite: false,
depthTest: false,
blending: THREE.AdditiveBlending,
uniforms: {
uColor: {
value: new THREE.Color(color) // 颜色
},
uRange: {
value: range || 100 // 显示当前范围的个数
},
uSize: {
value: size // 粒子大小
},
uTotal: {
value: number // 当前粒子的所有的总数
},
time: {
value: 0 //
}
},
vertexShader: `
attribute float index;
attribute float current;
uniform float time;
uniform float uSize;
uniform float uRange; // 展示区间
uniform float uTotal; // 粒子总数
uniform vec3 uColor;
varying vec3 vColor;
varying float vOpacity;
void main() {
// 需要当前显示的索引
float size = uSize;
float showNumber = uTotal * mod(time, 1.1);
if (showNumber > current && showNumber < current + uRange) {
float uIndex = ((current + uRange) - showNumber) / uRange;
size *= uIndex;
vOpacity = 1.0;
} else {
vOpacity = 0.0;
}
// 顶点着色器计算后的Position
vColor = uColor;
vec4 mvPosition = modelViewMatrix * vec4(position, 1.0);
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * mvPosition;
// 大小
gl_PointSize = size * 300.0 / (-mvPosition.z);
}`,
fragmentShader: `
varying vec3 vColor;
varying float vOpacity;
void main() {
gl_FragColor = vec4(vColor, vOpacity);
}`
});
const point = new THREE.Points(geometry, shader);
return point;
}使用案例
js
import Fly from './fly.js'
let uTime = {
value:0,
}
const flyData = {
source: {
x: 173,
y: 0,
z: 43,
},
target: {
x: 52,
y: 0,
z: 12,
},
range: 100,
height: 100,
color: "rgb(29,135,240)",
speed: 1,
size: 5,
};
const flyMesh = Fly(flyData);
flyMesh.material.uniforms.time = uTime;
const clock = new THREE.Clock(); //计时器
const FPS = 60; // 指的是 30帧每秒的情况
const singleFrameTime = 1 / FPS;
let timeStamp = 0;
function animate() {
window.loopId = requestAnimationFrame(animate);
const delta = clock.getDelta(); //获取距离上次请求渲染的时间
uTime.value += delta;
if (timeStamp > singleFrameTime) {
renderer.render(scene, camera);
// 剩余的时间合并进入下次的判断计算 这里使用取余数是因为 当页页面失去焦点又重新获得焦点的时候,delta数值会非常大, 这个时候就需要
timeStamp = timeStamp % singleFrameTime;
}
}效果展示
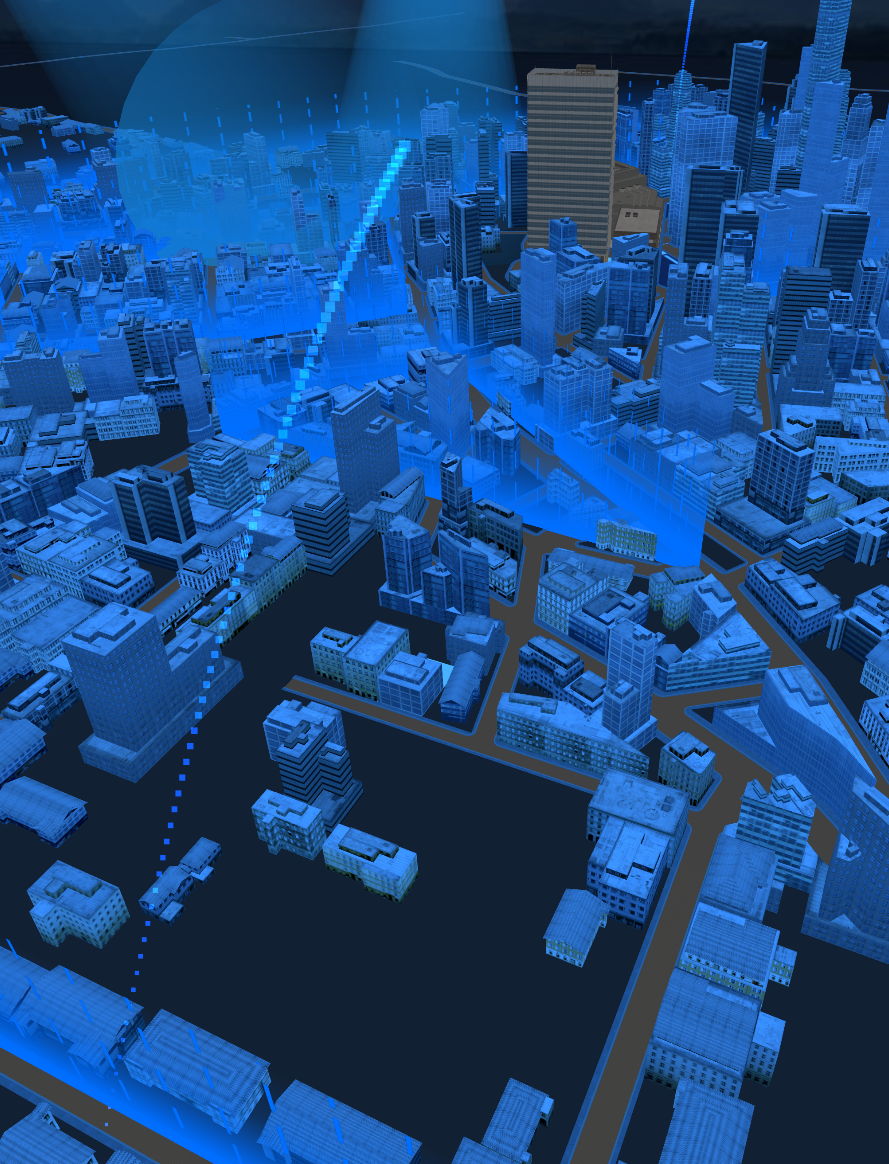
 小江的网站
小江的网站